Sustainability
Mechanical Recycling

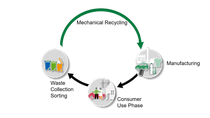
Mechanical recycling moves the circular economy
Mechanical recycling is an essential component of the circular economy. It can be applied to various material classes like plastics, lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles, or metals. End-of-life materials can be processed via collecting, sorting, shredding, melting and transforming it into secondary raw materials for a new application. Manufactured from recycled material, the article enters its new use-phase before the next end-of-life management.
For plastic waste, mechanical recycling is the preferred recycling solution if ecologically most beneficial, technologically possible, and economically attractive. Chemical recycling will complement mechanical recycling.
But there is more than plastics: BASF also engages in the recycling of precious metals and lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles. Find out more below.