BASF in Greater China 2023
Energy efficiency & environmental protection
We are committed to energy efficiency and global climate protection in this energy-intensive industry. We aim to significantly reducing our carbon footprint through our carbon management programs, which include adopting advanced technologies and processes, constantly upgrading facilities, and increasing our use of renewable energies. Our production processes are being optimized to be as energy efficient as possible with the help of comprehensive energy management.
- Total energy consumption increased as a result of overall higher production
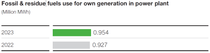
The total energy consumption of BASF sites in Greater China in 2023 increased, primarily due to the higher production compared to 2022. Overall higher production led to higher consumption of electricity, steam and residue fuel and fossil fuel. Electricity consumption increased by 0.4% to 1.164 million megawatt hours (MWh) in 2023 (2022: 1.159 million MWh). Steam supply totaled 3.229 million megawatt hours, 4.5% more than 2022 (2022: 3.091 million MWH). The usage of fossil and residue fuels in power plants for production was 0.954 million MWh in 2023, 2.9% higher than last year (2022: 0.927 million MWh).


Emissions to air
- Decrease in greenhouse gases (GHG) due to effective carbon management
BASF aims to achieving net zero emissions by 20501. By 20301, we aim to reducing our global greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 1 and 2) by 25% compared with 2018. We have implemented various measures in all BASF sites in Greater China to contribute to this ambitious goal.
In 2023, GHG emissions from BASF’s chemical operations in Greater China totaled 0.968 million metric tons, down by 10.7% compared with last year (2022: 1.176 million) despite higher production output. The CO2 emission reduction was greatly contributed by the ongoing initiatives by all the Greater China sites. One of the key CO2 emission initiatives involved a particular site which has continuously implemented initiatives to reduce CO2 emissions for the whole operation process through the applying sustainability solutions, use of digital applications, innovative technology development and production technical optimization. It involved the whole process from recycled raw materials application, optimization of packaging materials, transportation, to energy application and optimization of production processes. The good initiatives were shared as best practices with other sites.
1 Scope 1 and Scope 2 (excluding the sale of energy to third parties, including offsetting). The target includes greenhouse gases according to the Greenhouse Gas Protocol, which are converted into CO2 equivalents (CO2e).
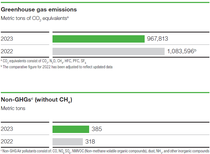
Aside from greenhouse gas emissions, BASF also monitors non-GHG air pollutants such as inorganic compounds like carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx) and ammonia, as well as dust or non-methane volatile organic compounds (NMVOC). Air pollutants from BASF’s chemical operations in Greater China were 385 metric tons (up by 21% compared with 318 metric tons in 2022).
In order to further reduce the volatile organic compounds (VOC) emitted from fugitive emission, one site in Greater China had implemented a “Leak Hunter” program whereby they want to achieve a zero loss of containment at the site. Site employees implemented a constant identification of any leak program and immediately rectify the leak if applicable. This not only reduces the fugitive emissions from the site operations but also improves the overall safe operations of the site itself.
Read more information about Emission to air at BASF Greater China 2023 Report
Water
- Sustainable water management with mandatory protection plans
- Using water responsibly
Water is a precious and critical resource in the chemical industry. It is used as a coolant, a solvent, a cleaning agent, and in the manufacturing of our products. BASF has set global goals for sustainable water management, including the responsible use of water in our production sites’ water catchment areas and along the entire value chain. BASF sites in Greater China adhere to group requirements that are aligned with the globally applicable standards and are exploring associated initiatives. The European Water Stewardship (EWS) Project has been completed at 15 BASF locations in water-stressed parts of Greater China, with three more sites planned by 2030.
To avoid unforeseen emissions and the pollution of surface or groundwater, BASF developed a water protection strategy for each manufacturing site, as a mandatory part of the global Responsible Care® initiative, of which BASF is a member. The wastewater protection plan involves assessing the risks of wastewater and drawing up suitable monitoring methods. Wastewater risk assessment helps identify the potential risks of unexpected wastewater releases. Regular audits are carried out to ensure that appropriate measures are implemented and complied with.

BASF has set global goals for sustainable water management, including the responsible use of water in our production sites’ water catchment areas and along the entire value chain.
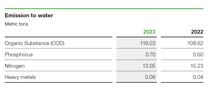
Emissions of water pollutants in Greater China increased in 2023 compared with 2022, mainly due to the higher production in 2023. Emissions of organic substances (COD) totaled 119.0 metric tons (2022: 108.6 metric tons). Phosphorus emissions were at 0.7 metric tons (2022: 0.6 metric tons). Nitrogen emissions were at 13.1 metric tons (2022: 15.2 metric tons), while heavy metal emissions rose to 0.06 metric tons (2022: 0.04 metric tons). Increase of water pollutants of COD, phosphorus and heavy metals were due to overall higher production volume while nitrogen decreased in 2023 due to installed higher nitrogen removal at a particular high emitter site.
The total water supply was 12.37 million cubic meters in 2023 (2022: 11.99 million cubic meters). Among them, 5.66 million cubic meters were used in production (2022: 5.67 million cubic meters), with the remaining predominantly used for cooling purposes. We conserve water by recirculating as much water as possible. The recirculated water used for cooling at BASF’s Greater China sites amounted to 660 million cubic meters in 2023 (2022: 621 million cubic meters).
Read more information about Water at BASF Greater China 2023 Report

Wastes

- Continuous efforts to reduce and recycle waste
- Audits of external waste management companies
BASF strives to design products and processes that minimize waste as much as possible. If waste is unavoidable, we explore recycling or energy recovery options at BASF’s existing Verbund site. Waste from BASF’s chemical operations in Greater China totaled 96,680 metric tons in 2022, a significant 11.7% drop from the year before (2021: 109,489 metric tons).
One site in Shanghai optimized the wastewater pre-treatment process to limit the generation of hazardous waste. In 2022, the total amount of waste recovered was at 69,378 metric tons (2021: 79,598 metric tons); while the total waste disposed was at 27,302 metric tons (2021: 29,891 metric tons).
External waste management providers are audited on a regular basis to ensure that hazardous waste is appropriately processed and disposed of. Since 2013, we have been closely monitoring the soil and groundwater status of all sites in Greater China.






