Edifícios iguais a centrais elétricas

Construção sustentável é a palavra da moda entre os arquitetos. No entanto, para a maioria de nós que vivem em casas construídas décadas atrás, a realidade está longe de ser os desenhos futuristas - nossas casas devoram energia, sendo muitas vezes sinônimo de desperdício e ineficiência. Mas isso pode estar prestes a mudar, pois empresas e universidades se unem para forjar uma nova paisagem urbana, onde os edifícios se tornam as centrais elétricas do futuro.
Pergunte aos principais cientistas de tecnologia ambiental de ponta para descreverem a casa do futuro e eles vão levá-lo para um mundo fascinante, onde o material e as ciências biológicas operam em harmonia para criar um ambiente construído vivo.
É um mundo onde as tecnologias miríades substituem os combustíveis fósseis e a energia nuclear. Um futuro onde a química, a biologia, a nanotecnologia, a ciência dos materiais e o biomimetismo fundem-se para criar uma cidade viva, interligada. Um lugar onde a energia solar é colhida de diferentes formas de cada fachada e armazenada de maneira intersazonal, onde o isolamento inteligente regula o ambiente, enquanto as paredes vivas de algas reagem com a luz solar para criar sombra e luz. Um mundo interconectado, onde a casa, o local de trabalho, o carro e a escola imitam um organismo vivo, interagindo naturalmente com o ambiente para captar a energia vinda de casas de dia e locais de trabalho a noite, para ser bombeada para onde ela é mais necessária.
A maioria dessas inovações recentes foi impulsionada pela ameaça das mudanças climáticas. Uma pesquisa feita pelo Programa das Nações Unidas para o Ambiente revela que construções mais inteligentes oferecem uma oportunidade única de fornecer cortes de custo-benefício nas emissões de gases de efeito estufa prejudiciais. Os prédios no mundo todo consomem 40% dos nossos recursos energéticos e emitem um terço dos gases de efeito estufa do planeta - um número que deve subir conforme a migração das populações carentes de energia para as cidades.
“Podemos fazer células solares em qualquer coisa, incluindo papel."
Dra. Trisha Andrew, Professora Assistente de Química da Universidade de Wisconsin-Madison
O problema com a visão sedutora de futuro dos cientistas é que, para a maioria de nós tal visão tem pouca relação com a nossa experiência real de mundo construído. Se você vive em Berlim, Xangai, Rio ou Milwaukee, provavelmente estará cercado por edifícios que mudaram pouco em design ao longo dos últimos 100 anos e que usam uma tecnologia que pouco se desenvolveu ao longo dos últimos 50 anos. A tecnologia mais avançada que vemos no uso cotidiano tende a ser limitada a painéis solares de silício cristalino pesado e turbinas eólicas.
Isso pode estar prestes a mudar. E o catalisador para a mudança é uma revolução silenciosa que vem ocorrendo nas salas de reuniões de grandes empresas e nos laboratórios de instituições acadêmicas. As pessoas estão percebendo que, enquanto não houver a falta de inovação brilhante na construção de design, não haverá foco suficiente sobre como trazer essas novas tecnologias para o mercado em geral. Essa percepção está levando algumas das melhores mentes científicas do mundo a mudar o pensamento tradicional para enfrentar o desafio tecnológico de escala. A questão é: como fazer com que esta tecnologia seja acessível e rentável e como produzi-la em escala grande o suficiente para realmente fazer a diferença.
Greg Keeffe, Professor de Arquitetura Sustentável e chefe de pesquisa da Universidade de Queens, em Belfast, na Irlanda, acredita que os arquitetos e designers podem ter algo a aprender com as técnicas de produção em massa utilizadas pelos fabricantes de automóveis. Ele diz que a necessidade de hoje de empinar casas para ocupar o pouco espaço urbano remanescente, significa que cada edifício tem que ser concebido individualmente. Isto não oferece oportunidade de desenvolver os tipos de inovação que vão ao encontro da produção em massa.
"Se você observar uma casa média com um Mercedes Classe E estacionado do lado de fora, a casa é muito fraca quando comparada ao carro", diz o professor Keeffe. "Eu acredito que precisamos de um produto de massa personalizado mais industrializado, que está atualmente fora do nosso alcance, pois os edifícios são projetados de modo diferente dos carros. Centenas de anos de reflexão dos homens serviram para projetar cada elemento de um carro, enquanto muito menos reflexão tem sido destinada para cada elemento de um edifício, porque cada edifício é tão individual."
Facts and figures: Energy consumption and energy efficiency
From lab experiment to industrial production

Recently set up to address this very challenge, the Sustainable Product Engineering Centre for Innovative Functional Industrial Coatings (SPECIFIC) is an industrial and academic consortium tasked with bridging the knowledge gap that exists between innovation and production. Launched four years ago, the project is led by Swansea University in Wales with funding from the Welsh and UK governments, as well as from its main industrial partners Tata Steel, NSG-Pilkington Glass and BASF.
SPECIFIC’s aim is to turn buildings into the powerhouses of the future. It plans to act as a link between UK universities to exploit cutting edge, global developments in building materials and design, using smart coatings that enable walls and roofs to collect, store and release renewable energy. Working mostly with steel and glass, the project has already experienced extraordinary advances that are set to revolutionize at least one sector of the construction industry.
Kevin Bygate is Chief Executive Officer of the SPECIFIC project, heading up a team of more than 120 world-class scientists, technologists, engineers and business developers, all focusing on how best to up-scale existing technology and so turn laboratory-scale innovations into products capable of being manufactured on a large scale.
“There are many universities and research institutes that make the initial inventive step. What that physically means is, they have created something the size of a thumbnail, and on the thumbnail is a small dot, the size of a pin, that does something interesting,” says Bygate. “We take over at that stage to replicate the function with an abundant material using a process that can be scaled up. We use pilot lines to produce one-meter-wide sheets and then a reel-to-reel line that will make a material large enough to put on a building.”
One product is the transpired solar collector, which is capable of absorbing an average 50%, and up to 75% in good conditions, of the solar energy that hits a building. Transpired solar collectors are installed as an additional micro-perforated steel skin onto an existing or new wall or roof, creating a cavity of heated air between the building’s surface and the metal skin. The heated air is drawn from the cavity and fed into the building, so that it can either be used to meet the building’s immediate energy needs, or be stored for later.
Partner in the project, Tata Steel, produces steel in the UK for building warehouses, supermarkets and retail outlets. SPECIFIC estimates that if just 10% of the steel produced each year by Tata Steel had this smart coating, it could produce 10 GW of power, or the equivalent of one nuclear power station’s annual energy output.
Bygate believes that transpired solar collectors could become a key future energy resource. “What we have is proof of concept and now we are looking at the business model to take it to market,” he says. “Depending on the rate of public acceptance for the product and the adoption curves, you could generate around one third of the UK’s renewables by the 2020s using this type of technology.”
As important as harvesting solar energy is its storage. Batteries, hot water storage and underground thermal storage all have potential, but tend to take up large amounts of space. While some energy needs to be stored for a matter of hours before being used, other energy needs to be drawn on inter-seasonally, typically stored in summer for use in winter.
SPECIFIC is having success on this front too. Professor Dave Worsley, who heads the project’s academic research program, explains: “What we are working on is a thermochemical store – the basis of which is a salt that absorbes or releases water, similar to the way we sweat – which traps or releases a huge amount of energy.”
It is this ability to trap and release energy so efficiently that Worsley believes will make this solution suitable for inter-seasonal storage, while taking up ten times less space than using water for energy storage.
Solar paint
For years, scientists have been predicting the creation of an affordable photovoltaic paint that could be used on homes to harvest solar energy. But the reality is that it will still be many years before such a product reaches the market. But the work being carried out by Dr. Trisha Andrew, Assistant Professor of Chemistry at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, has taken us one step closer.
Organic photovoltaic devices that can be incorporated into a dye have been around since the 1990s. Made from materials such as carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and sulfur, these devices have the merit of being inexpensive to produce, but suffer from inefficiency and a short life expectancy in comparison to silicon-based materials.
A couple of years ago, Andrew and her colleagues had a “eureka” moment. Why not make a virtue of this and produce a photovoltaic material, capable of powering electronic devices, but so cheap to manufacture that you just replace it when it degrades?
“For example, if you are creating CO2 emissions on your site, you can take those emissions and feed them into the façade.”
Associate Director Dr.-Ing. Jan Wurm, Arup’s head of Europe research and lead on the BIQ (Bio Intelligent Quotient) house

“The question we had never asked ourselves before was, how can you make these materials commercially,” explains Andrew. “It is a question that pharmaceutical companies ask every day. We were following the same process of chemical synthesis, so the logical step for us was to ask what is the effect on price per peak watt of your chemical synthesis?”
By focusing on the manufacturing process, Andrew discovered they were already sitting on a commercially viable product, capable of powering household devices with solar energy. At a production cost of less than 50 U.S. cents each, it would not matter that the photovoltaic cells had a life expectancy of between six months and two years.
“We now have a very promising set of advanced results on which we have built a start-up company. We can make solar cells on anything, including paper. That’s something you just can’t do with silicon,” says Andrew. “Scientifically and logically a paint is within our reach. If phase one goes well, a paint will be coming down the line, but it will probably be no earlier than a decade from now.”
Green-skinned buildings
Every now and then a new technology emerges that changes the way we think about buildings. Showcased at the Hamburg International Building Exhibition, the world’s first “bioadaptive façade” house has had such an impact. It opens up exciting new opportunities for architects and designers to break down barriers between the material and biological world and so takes us that bit closer to the vision of a living city.
Known as the BIQ (Bio Intelligent Quotient) house, it is the result of collaboration between a group of architects, engineering and design companies, including international consultants Arup.
Associate Director Dr.-Ing. Jan Wurm, Arup’s head of Europe research and lead on the BIQ house, describes the new technology as “bio-utilisation”. “We are creating micro-algae to generate heat and biomass, so it is a biological process just like a plant or a tree growing. It all follows on from the same photosynthesis, it’s just that we do it in a controlled environment,” explains Wurm.
The BIQ house features a façade, composed of bioreactor façades, that traps micro-algae in water between two plates of glass. Exposed to sunlight, the micro-algae double their mass every seven hours through photosynthesis. This green “skin” creates a natural shade to cool the inside of the building.
The algae also provide the house with two possible sources of energy. The first is the solar thermal heat captured by the water trapped between the glass plates. The sun’s rays heat the water and, as it contains green algae, it heats faster than clear water. The heat can be drawn out of the water as it passes through a pump room and then stored underground for future use. The second energy source comes from harvesting the algae themselves. To do this, oxygen is pumped through a central floatation device so that the algae can be skimmed off the surface. The algae can also be fed into the building’s biomass plant to create methane as a power source.
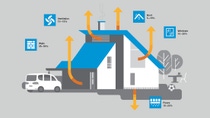
“The system brings together different flows and cycles, such as water, carbon, heat and even food, if you want. So you can create an industrial symbiosis,” explains Wurm. “For example, if you are creating CO2 emissions on your site, you can take those emissions and feed them into the façade.” It is this idea of the building being incorporated into the natural cycles of its environment, along with the opportunity to design with a living façade that changes throughout the day, that is exciting architects.
“What is interesting about it is the turbulence from the rising bubbles, but also the way that it changes color throughout the day and across seasons. You can use reflecting glass on the back so the bubbles create a glare effect, print interlayers, whatever you like,” he says.
There is clearly no single silver bullet solution to our energy problems. The powerhouse of the future will be a mixture of many technologies. The bioreactor façade is designed to work in harmony with other energy transformation techniques.
It is here that Wurm talks of the interconnected city, the city as an organism where different technologies exchange and provide usable energy in symbiotic networks. It is here that the living city starts to take shape, which is why bioreactor façades are generating so much interest.
Keeping heat in
But what about existing buildings? While transpired solar collectors and third generation photovoltaic could, in the future, be adapted for retrofitting, bioreactor façades are not the kind of thing that can be bolted to the front of your average home.
One cutting edge development that is being targeted at the domestic retrofit market is smart insulation. Increasing thermal efficiency without compromising aesthetics is the key goal. BASF has, for decades, developed insulation materials with different characteristics. Over the past seven years, it has been working on a new form of insulating material, called SlentiteTM, that contains pores on a nanoscale.
Now at the pilot production stage, it is a pure polyurethane aerogel that has all the necessary strength and provides high efficiency insulation, while being between 25 to 50% thinner than an equivalent insulation. Its unique quality is its ability to absorb and release water vapor, regulating moisture inside the building. “We see retrofit as well as new builds as its main application, both as an interior and exterior insulation,” explains Dr. Marc Fricke, who heads the team at BASF that created the new material.
Cool ideas
The Passive House in China

Insulation has been a driving force for one of the most significant recent developments in sustainable housing – the Passive House. A German concept, the Passive House provides an airtight, highly insulated shell that can reduce heat loss to the point where year-round comfort is achieved without a heating system.
It is a concept that has caught the attention of the Landsea Group, one of China’s largest real estate companies, which opened the country’s first Passive House, the Bruck project, in April this year.
Built in Changxing County, Zhejiang Province in Southern China, an area known for its cold winters, extremely warm summers and high humidity, the Bruck project is a hotel for delegates visiting a nearby research centre which showcases the Passive House concept. Landsea believes that if it can demonstrate that the Passive House works in Changxing’s difficult climate, then it could be adopted in other parts of China. “These technologies could be widely applied in China, but we need to select the most suitable design and technologies according to local conditions in each different climate zone,” explains Kai Zou, Civil and Sustainability Engineer at Landsea.
With the Chinese government placing more emphasis on the need for sustainable housing, China’s construction industry is becoming more receptive to new ideas about reducing energy consumption. Landsea believes that now is the right time to champion the idea of the Passive House in one of the biggest housing markets in the world.
Algae façades, photovoltaic paints, smart walls and roofs, living buildings that do away with conventional energy sources – all this may still sound futuristic. But if the new breed of entrepreneurs and academics are successful, these cutting edge technologies will be appearing in buildings where we live sooner than we think.




